Appearance
元认知与自我管理
点击上方图片可观看原课程视频。
引言
本节面向想要了解“智能体如何反思自身行为”的学习者。完成学习后,你将掌握元认知的关键概念,并能在智能体设计中应用相关技巧。
学习目标
- 理解在智能体定义中引入推理循环的影响;
- 运用规划与评估手段,构建可自我纠错的智能体;
- 设计能够动态生成与修改代码的智能体。
元认知基础
元认知(Metacognition)指的是“对自己思考过程的思考”。对于智能体而言,这意味着具备以下能力:
- 监控自身的内部流程;
- 根据自我感知与过往经验调整行为;
- 自主诊断并修正错误。
这类能力有助于提升透明度、推理深度、适应性与感知准确度。例如:
- 透明性:智能体能解释自己的推理过程;
- 推理:智能体可综合信息做出更合理的决策;
- 适应:智能体能根据环境变化调整策略;
- 感知:智能体能更准确地理解外部数据。
什么是元认知?
元认知强调“明确自己为何做出某个选择”,例如:
- “我优先推荐价格更低的航班,但可能错过直达航班,所以需要重新检查”;
- 记录自己为何选择某条路线;
- 发现“总是过度依赖用户之前的偏好”,从而调整策略而非只改最终推荐。
元认知的重要性
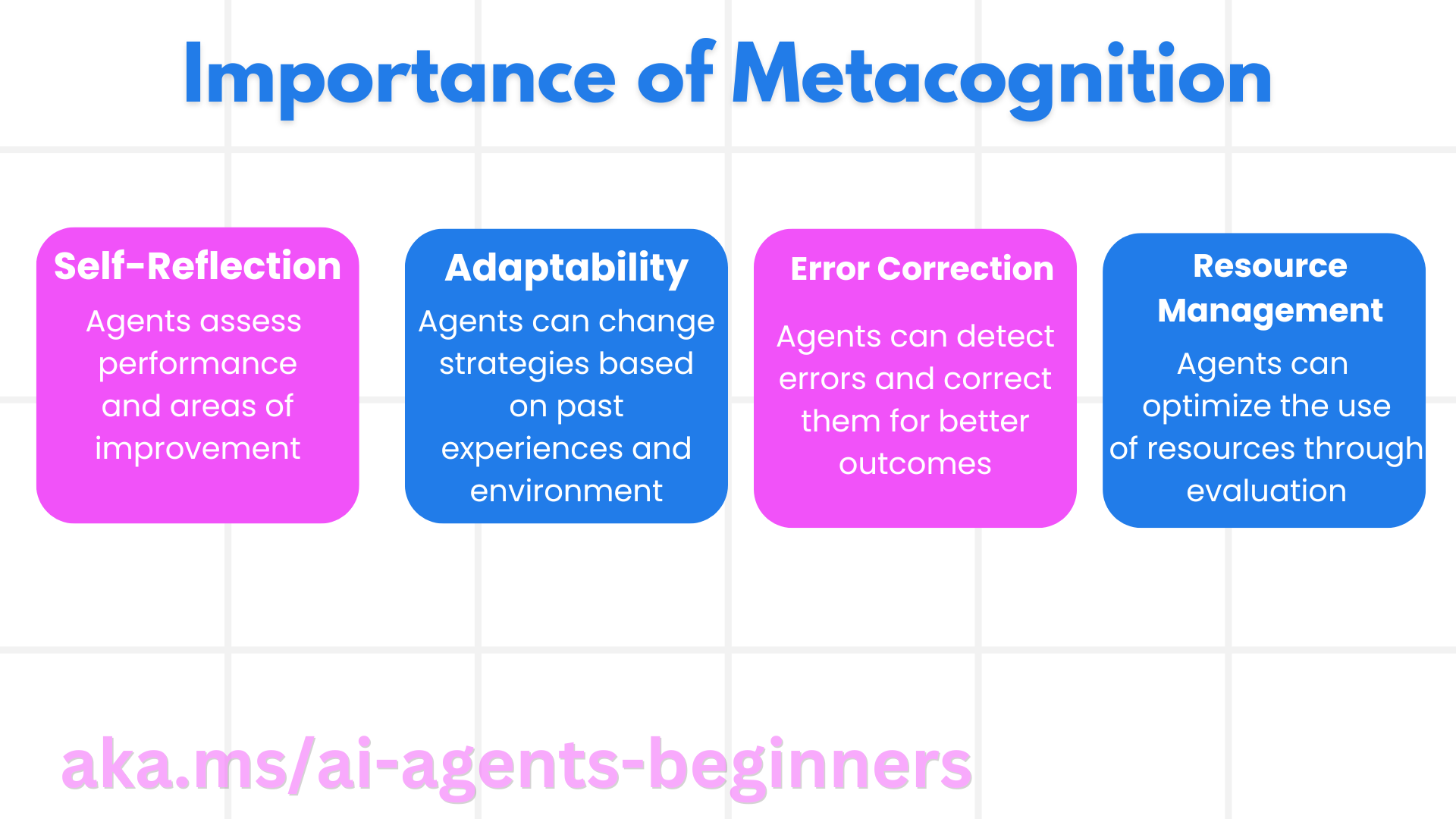
- 自我反思:评估表现并找出改进方向;
- 适应性:依据经验与环境变化调整策略;
- 纠错能力:自主发现并修正错误;
- 资源管理:通过规划与评估更高效地使用时间与算力。
智能体的核心组成
一个智能体通常由以下部分构成:
- 角色(Persona):决定与用户互动的方式;
- 工具(Tools):智能体可调用的外部能力与函数;
- 技能(Skills):智能体具备的知识与经验。
这些要素组合成一个“专业单元”。例如一个旅行智能体不仅规划行程,还会根据实时数据与过往反馈随时调整方案。
旅行智能体中的元认知示例
设想一个名为 “Travel Agent” 的旅行助手,其目标是为用户规划巴黎行程。为了具备元认知能力,它需要在执行过程中不断评估并调整策略。
当前任务:帮助用户规划巴黎之旅。
基本步骤:
- 收集用户偏好。
- 检索航班、酒店、活动等信息。
- 生成初步推荐。
- 获取用户反馈。
- 基于反馈调整策略,持续优化。
以下代码片段演示了 Travel Agent 的基本结构:
python
class Travel_Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.user_preferences = {}
self.experience_data = []
def gather_preferences(self, preferences):
self.user_preferences = preferences
def retrieve_information(self):
flights = search_flights(self.user_preferences)
hotels = search_hotels(self.user_preferences)
attractions = search_attractions(self.user_preferences)
return flights, hotels, attractions
def generate_recommendations(self):
flights, hotels, attractions = self.retrieve_information()
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions)
return itinerary
def adjust_based_on_feedback(self, feedback):
self.experience_data.append(feedback)
self.user_preferences = adjust_preferences(self.user_preferences, feedback)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
1. 元认知驱动的规划
规划是智能体达成目标的关键。它包括明确任务、拆解步骤、识别所需资源与运用经验。
Travel Agent 的规划流程
- 收集用户偏好(时间、预算、兴趣等);
- 搜索符合条件的航班、住宿、景点;
- 生成个性化行程;
- 向用户展示并征求反馈;
- 根据反馈调整方案;
- 确认后执行预订;
- 在旅行前与行程中持续提供支持。
示例交互代码:
python
travel_agent = Travel_Agent()
preferences = {
"destination": "Paris",
"dates": "2025-04-01 to 2025-04-10",
"budget": "moderate",
"interests": ["museums", "cuisine"]
}
travel_agent.gather_preferences(preferences)
itinerary = travel_agent.generate_recommendations()
print("Suggested Itinerary:", itinerary)
feedback = {"liked": ["Louvre Museum"], "disliked": ["Eiffel Tower (too crowded)"]}
travel_agent.adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2. Corrective RAG(检索增强生成的纠错模式)
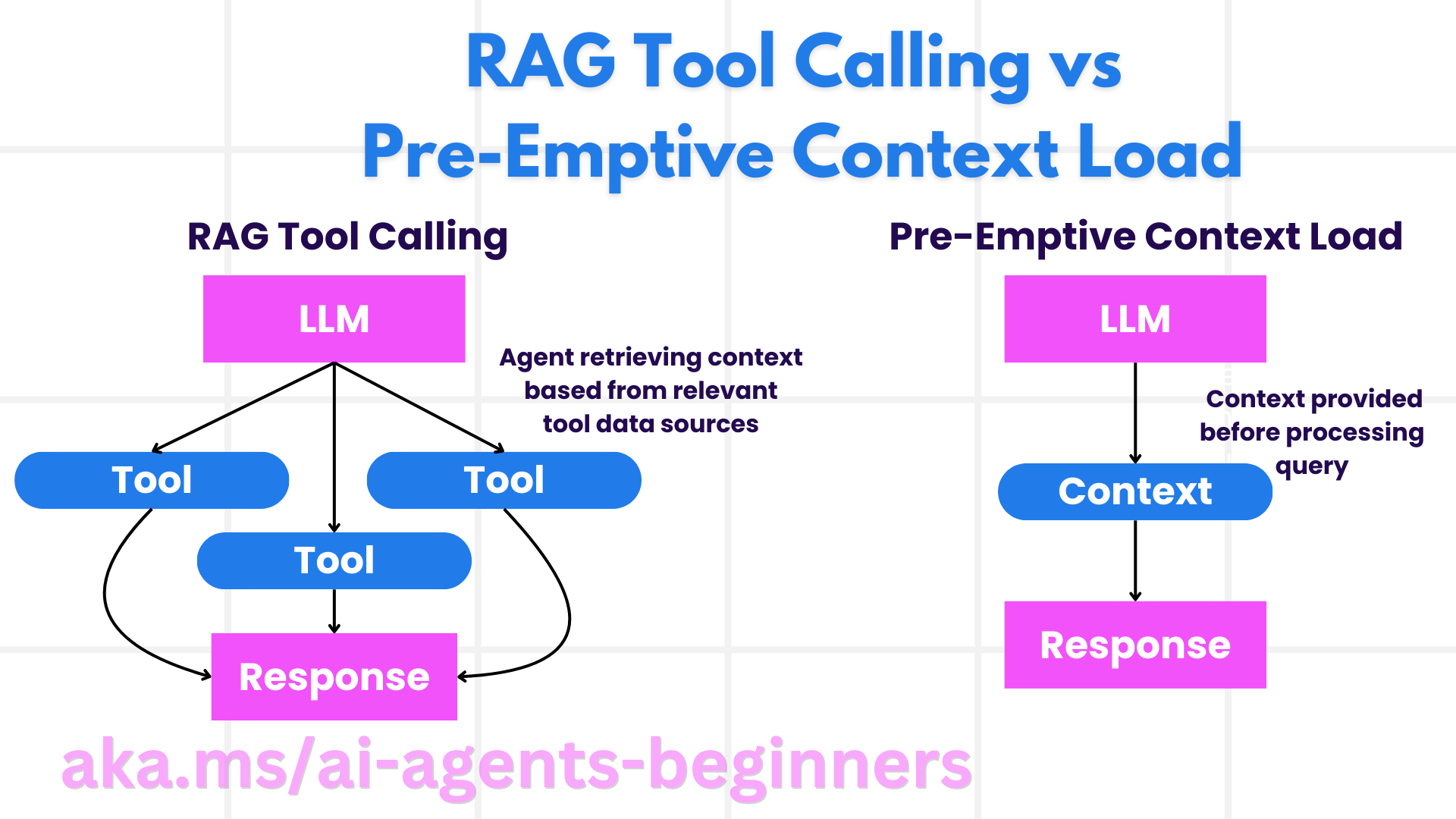
- RAG:结合检索与生成,先检索相关文档,再交由生成模型给出回答。
- 预加载上下文:提前载入背景信息,避免实时检索。
Corrective RAG 的核心
- 提示技术:通过特定提示引导模型检索相关信息;
- 工具实现:利用算法评估检索结果的相关性;
- 评估反馈:持续评估表现并修正偏差。
以 Travel Agent 为例,完整流程如下:
python
class Travel_Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.user_preferences = {}
self.experience_data = []
def gather_preferences(self, preferences):
self.user_preferences = preferences
def retrieve_information(self):
flights = search_flights(self.user_preferences)
hotels = search_hotels(self.user_preferences)
attractions = search_attractions(self.user_preferences)
return flights, hotels, attractions
def generate_recommendations(self):
flights, hotels, attractions = self.retrieve_information()
itinerary = create_itinerary(flights, hotels, attractions)
return itinerary
def adjust_based_on_feedback(self, feedback):
self.experience_data.append(feedback)
self.user_preferences = adjust_preferences(self.user_preferences, feedback)
new_itinerary = self.generate_recommendations()
return new_itinerary1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
预加载上下文示例
python
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.context = {
"Paris": {"country": "France", "currency": "Euro", "language": "French", "attractions": ["Eiffel Tower", "Louvre Museum"]},
"Tokyo": {"country": "Japan", "currency": "Yen", "language": "Japanese", "attractions": ["Tokyo Tower", "Shibuya Crossing"]},
"New York": {"country": "USA", "currency": "Dollar", "language": "English", "attractions": ["Statue of Liberty", "Times Square"]},
"Sydney": {"country": "Australia", "currency": "Dollar", "language": "English", "attractions": ["Sydney Opera House", "Bondi Beach"]}
}
def get_destination_info(self, destination):
info = self.context.get(destination)
if info:
return f"{destination}:\nCountry: {info['country']}\nCurrency: {info['currency']}\nLanguage: {info['language']}\nAttractions: {', '.join(info['attractions'])}"
else:
return f"Sorry, we don't have information on {destination}."1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
以目标为导向的引导式迭代
通过预先设定目标,再结合迭代优化,可持续提升推荐质量:
python
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self, destinations):
self.destinations = destinations
def bootstrap_plan(self, preferences, budget):
plan = []
total_cost = 0
for destination in self.destinations:
if total_cost + destination['cost'] <= budget and self.match_preferences(destination, preferences):
plan.append(destination)
total_cost += destination['cost']
return plan
def match_preferences(self, destination, preferences):
for key, value in preferences.items():
if destination.get(key) != value:
return False
return True
def iterate_plan(self, plan, preferences, budget):
for i in range(len(plan)):
for destination in self.destinations:
if destination not in plan and self.match_preferences(destination, preferences) and self.calculate_cost(plan, destination) <= budget:
plan[i] = destination
break
return plan1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
利用 LLM 进行重排与打分
通过调用 Azure OpenAI,对候选目的地进行重排:
python
class TravelAgent:
def __init__(self, destinations):
self.destinations = destinations
def get_recommendations(self, preferences, api_key, endpoint):
prompt = self.generate_prompt(preferences)
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json", "Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}"}
payload = {"prompt": prompt, "max_tokens": 150, "temperature": 0.7}
response = requests.post(endpoint, headers=headers, json=payload)
recommendations = response.json()['choices'][0]['text'].strip().split('\n')
return recommendations1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
RAG:提示 vs. 工具
| 侧面 | 提示技巧 | 工具 |
|---|---|---|
| 控制方式 | 手动编写提示触发检索 | 自动化检索与生成 |
| 灵活性 | 可针对具体需求自定义 | 更适合大规模流程 |
| 复杂度 | 需调试提示模板 | 更易嵌入整体架构 |
3. 评估相关性与意图搜索
相关性评分示例
python
def relevance_score(item, query):
score = 0
if item['category'] in query['interests']:
score += 1
if item['price'] <= query['budget']:
score += 1
if item['location'] == query['destination']:
score += 1
return score1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
意图识别与结果个性化
python
def identify_intent(query):
if "book" in query or "purchase" in query:
return "transactional"
elif "website" in query or "official" in query:
return "navigational"
else:
return "informational"1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
4. 代码生成型智能体
代码生成智能体可自动编写并执行代码,用于数据分析、SQL 检索等。
示例:根据用户偏好生成请求代码、执行并获取实时数据,随后生成行程并根据反馈调整。
python
def generate_code_to_fetch_data(preferences):
code = f"""
def search_flights():
import requests
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/flights', params={preferences})
return response.json()
"""
return code1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5. 利用环境上下文的推理
通过 schema 信息引导偏好调整,提升查询准确性:
python
def adjust_based_on_feedback(feedback, preferences, schema):
if "liked" in feedback:
preferences["favorites"] = feedback["liked"]
if "disliked" in feedback:
preferences["avoid"] = feedback["disliked"]
for field in schema:
if field in preferences:
preferences[field] = adjust_based_on_environment(feedback, field, schema)
return preferences1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
6. SQL 作为 RAG 技术
通过 SQL 查询快速检索数据库中的航班、酒店与景点数据:
python
def generate_sql_query(table, preferences):
query = f"SELECT * FROM {table} WHERE "
conditions = [f"{key}='{value}'" for key, value in preferences.items()]
query += " AND ".join(conditions)
return query1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
元认知实现示例
以下示例展示了一个会“反思”自身策略的酒店推荐智能体:
python
class HotelRecommendationAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.previous_choices = []
self.corrected_choices = []
self.recommendation_strategies = ['cheapest', 'highest_quality']
def recommend_hotel(self, hotels, strategy):
if strategy == 'cheapest':
recommended = min(hotels, key=lambda x: x['price'])
elif strategy == 'highest_quality':
recommended = max(hotels, key=lambda x: x['quality'])
else:
recommended = None
self.previous_choices.append((strategy, recommended))
return recommended
def reflect_on_choice(self):
if not self.previous_choices:
return "No choices made yet."
last_choice_strategy, last_choice = self.previous_choices[-1]
user_feedback = self.get_user_feedback(last_choice)
if user_feedback == "bad":
new_strategy = 'highest_quality' if last_choice_strategy == 'cheapest' else 'cheapest'
self.corrected_choices.append((new_strategy, last_choice))
return f"Reflecting on choice. Adjusting strategy to {new_strategy}."
else:
return "The choice was good. No need to adjust."1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
该智能体能够:
- 记录自己的选择;
- 根据反馈判断结果好坏;
- 如果表现不佳,则调整策略,从而体现“自我反思”。
总结
通过引入元认知能力,智能体能够在规划、检索、生成与代码执行等环节持续自我评估与优化,从而提供更可靠、更个性化的服务。
常见问题交流
如需进一步讨论,欢迎加入 Azure AI Foundry Discord 参与问答或办公时间。